Gaming, AR and metaverse: Raffaella Camera talks about the digital future of branding
by Alessandro Mancini
The metaverse is no longer a distant prospect reserved only for those with a passion for technology. Today, this virtual dimension, enriched with the most advanced immersive technologies, has become an increasingly greater part of current society and is radically transforming the way in which brands interact with their consumers. Leading this revolution is Raffaella Camera, one of the main pioneers in immersive technology, gaming, and entertainment sectors; she has brought her vision to the 2024 Digital Design Days stage in Milan. Her career has been outstanding for its constant evolution in leadership roles in companies like Epic Games and Accenture, always with a clearly defined mission: shaping the future of marketing and digital experience.
Currently, Camera is involved in strategic consulting for the expansion of numerous companies in the gaming, artificial intelligence and entertainment sectors. Her aim is to develop innovative collaborations from a cultural viewpoint, to invent new intellectual property and products (IP), and to create brand name experiences in the most influential gaming platforms such as Roblox and Fortnite. It is her opinion that these platforms represent “new social hubs”, where consumers will not only interact with each other and with brands but will become an active part of the creative process and diffusion of the content.
The impact of gaming on the global stage has been enormous: today there are more than three billion gamers all over the world, a number that cannot be ignored by brands that are trying to build stronger and more authentic relationships with their customers. “Gaming platforms like Roblox and Fortnite offer interactive and immersive experiences to millions of users” explains Camera. “The total minutes spent on these platforms each day exceed the time spent on the most popular social media like TikTok, Facebook, Instagram and X. This tells us a lot about where the public is investing its time and attention”.
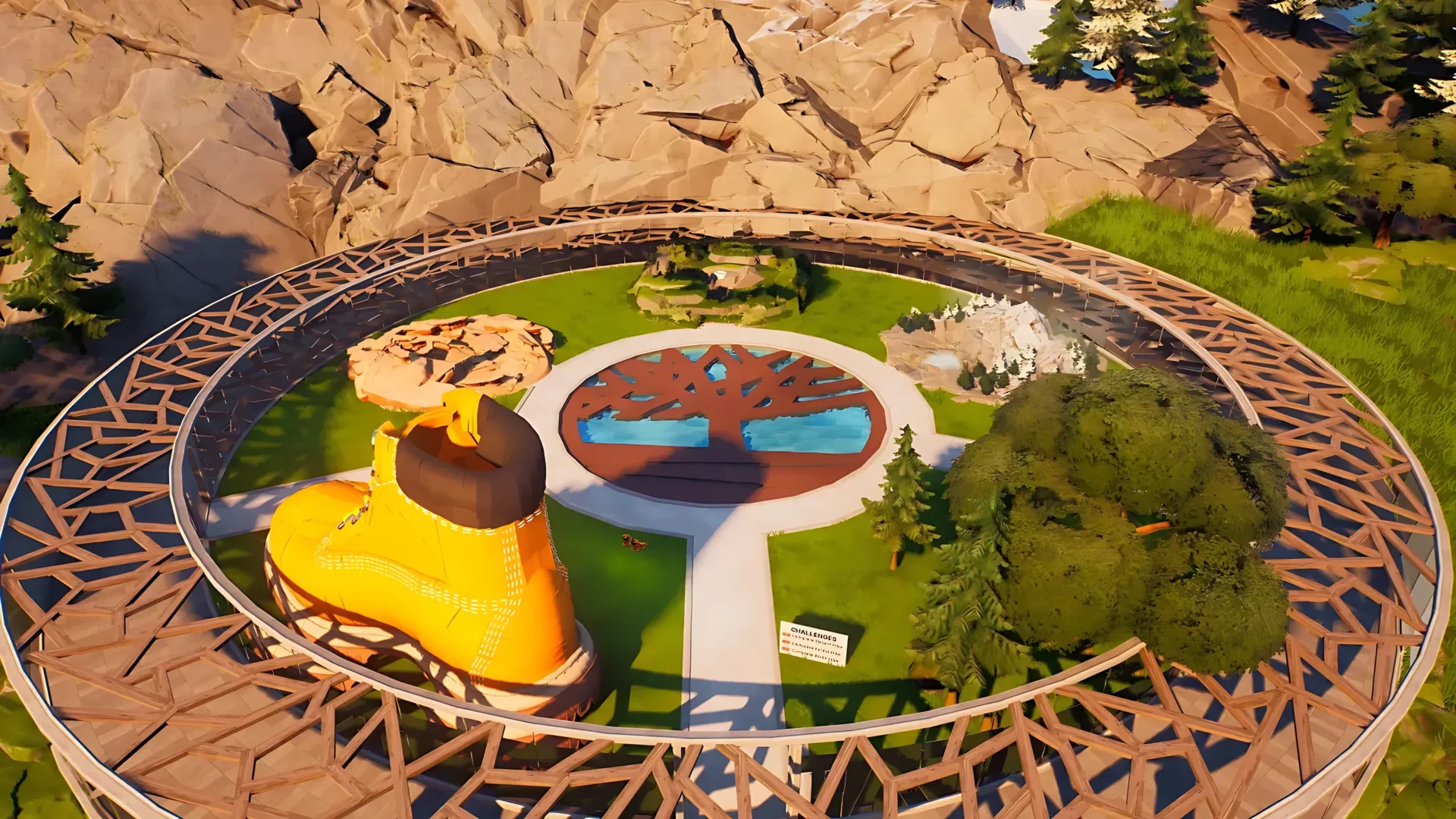
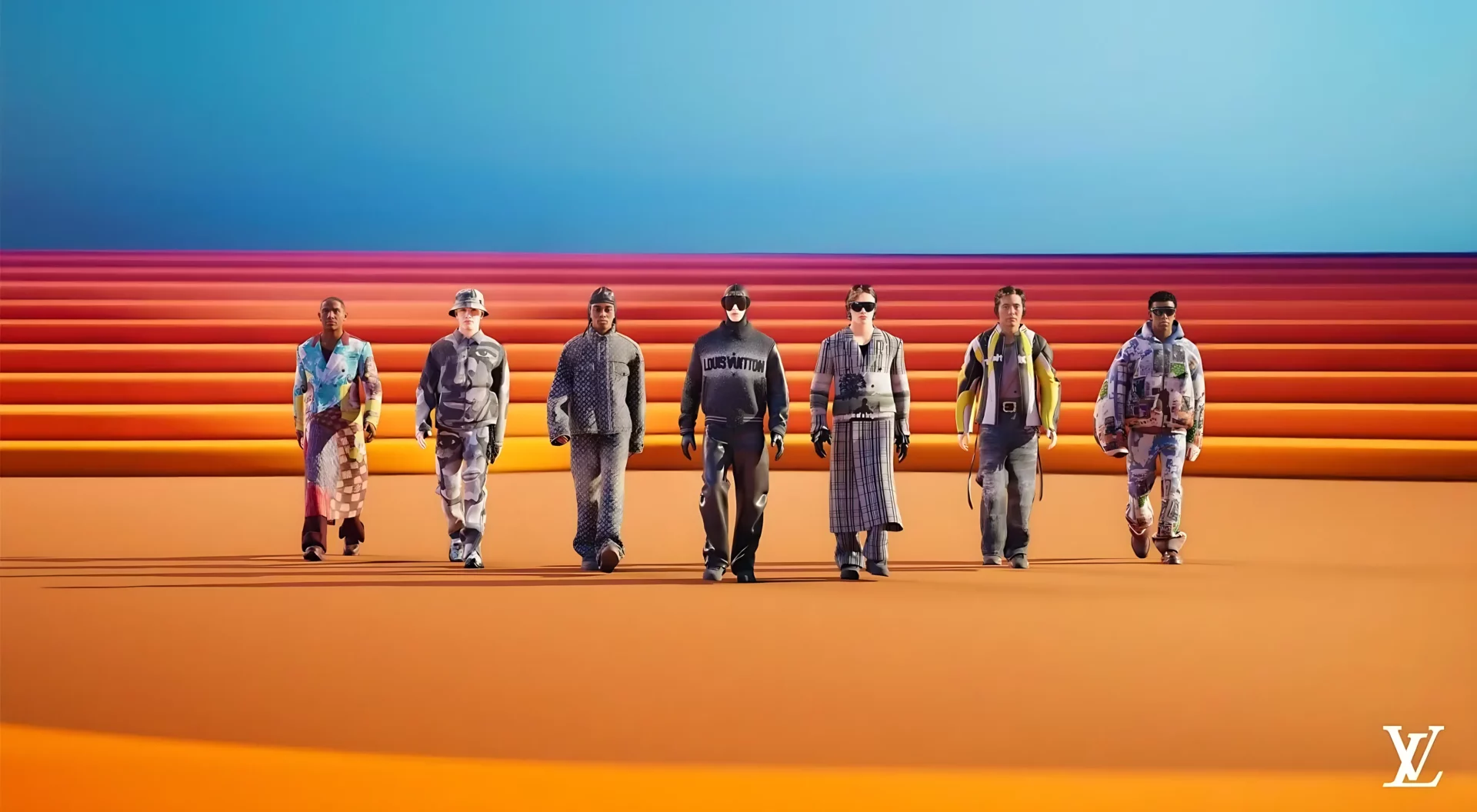
During her experience as Head of Brands for Unreal Engine at Epic Games, Camera worked in close contact with brands like LVMH and Timberland to help them build strong-impact, immersive experiences within Fortnite and on their branded channel. “Companies are beginning to learn how to take advantage of these virtual spaces, not just to launch products or events, but also to sell virtual goods, collect valuable data and direct traffic towards their online and retail stores”, Camera explains. In fact, many of these platforms permit brands to integrate their universe in worlds of existing games, thus facilitating a more direct and authentic connection with the public.
Camera continues:”One of the aspects that makes these technologies so powerful is their capacity to create personalised experiences. Today’s consumers are looking for something much more than passive entertainment. They want to be part of an experience and to contribute actively to its construction. This change is pushing brands to rethink their traditional marketing strategy with a greater focus on direct engagement and interactivity. It is a natural evolution: consumers are no longer simply message targets; they are becoming co-creators of the experiences they share”.
But the evolution does not stop here. Camera is focussing particular attention on the future of augmented reality (AR), a technology which, despite current hardware limitations, has the potential to revolutionise not just entertainment, but communications and social contact as well. “AR will allow us to break down the physical barriers and to connect with other people in completely new ways. Imagine a video call in Face Time but taken to a higher level where the digital presence becomes almost tangible”, she explains. However, Camera recognises that it will take several years before AR becomes a daily solution, accessible to all. But she is convinced that its impact will be strong and widespread.
As far as challenges are concerned, Camera underlines how the adoption of immersive technologies by companies is a complex process that demands vast reorganisation in their internal structures. “Each company needs to develop a bespoke 3D pipeline for its own products and services. This means rethinking the entire process, from design to production, from marketing to distribution”. According to Camera, the advantage of such a transformation lies in the ability to “create a library of reusable 3D resources that not only simplify internal processing, but also improve the connection with consumers in the digital space”. In fact, this kind of approach allows companies to be more flexible and ready to answer new market needs.
But which sectors does Camera consider will gain the greatest advantages by adopting immersive technology and the metaverse?
Today’s consumers are looking for something much more than passive entertainment. They want to be part of an experience and to contribute actively to its construction
Camera states: “Without a doubt, lifestyle and entertainment will continue to be the most influenced, however, the automotive industry is also exploring some fascinating possibilities. Think of how entertainment and 3D commerce could be integrated in self-driving vehicles. Or the fashion world, which is already experimenting with virtual make-up and clothing, connected to the customer’s avatar through 3D sensors.” These examples demonstrate how technology can enrich physical products, transforming them into digital experiences that expand the customer’s perceived value.
The musical industry is another environment which is exploring new paths thanks to these technologies. “Artists can now propose 3D tours and virtual concerts just as they did for ABBA. This type of experience does not only expand the potential public, but also offers new monetization opportunities through digital goods and personalised interaction with fans”. Camera feels that future possibilities are practically endless, but that only the more innovative companies will be able to take best advantage of them. Looking to the future, Camera remains convinced that brand success will depend on the companies’ capacity to adapt rapidly to new technologies and to integrate them into their business strategies. “Companies that are able to take advantage of gaming platforms and immersive technologies to create unique and engaging products and experiences will be those which will emerge successfully in the competitive panorama of the future” she concludes.
Ultimately, integration between the real and virtual has already begun and is revolutionizing not only the way companies communicate with consumers, but also the very concept of entertainment and products. Immersive technologies are opening a new chapter in the history of marketing and commerce, and with her vision and leadership, Raffaella Camera is a key figure in this revolution.
Alessandro Mancini
Is a graduate in Publishing and Writing from La Sapienza University in Rome, he is a freelance journalist, content creator and social media manager. Between 2018 and 2020, he was editorial director of the online magazine he founded in 2016, Artwave.it, specialising in contemporary art and culture. He writes and speaks mainly about contemporary art, labour, inequality and social rights